Dorithricin® -
Pharyngitis

Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is a painful inflammation of the mucosa of the throat. Pharyngitis (also known simply as "inflammation of the throat") is relatively common and usually occurs concurrently with an infection of the upper respiratory tract. Typical symptoms include a sore throat and difficulties swallowing. Targeted treatment is important to prevent complications.
![]() Tip:
Tip:
Dorithricin® can be used in any phase of a sore throat
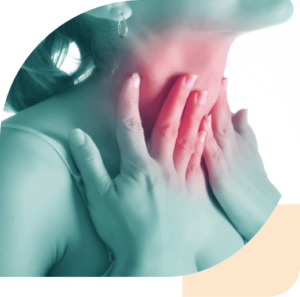
Pharyngitis: Causes
The pathogens that cause acute pharyngitis are generally viruses, less often bacteria:
| Viruses | |
| Rhinoviruses | Adenoviruses |
| Coronaviruses | Epstein-Barr virus |
| Bacteria |
| Beta-haemolytic group A streptococci = GAS |
| Beta-haemolytic group C and G streptococci |
Persistent irritation of the mucosa, rather than viruses or bacteria, is generally the cause of chronic pharyngitis. This kind of irritation can be triggered by various factors, for example:
- Dust
- Nicotine
- Alcohol
- Chemicals
- Irritant gases
In addition, chronic pharyngitis may also be caused by impaired nasal breathing (e.g. due to a deviated nasal septum): Those affected mainly breathe through the mouth.
Pharyngitis: Symptoms
The following symptoms are typical of acute pharyngitis:
- Sore throat
- Swallowing difficulties
- Possibly cough
- Possibly runny nose
- Fever
- Reddened mucosa in the throat
If a bacterial infection is suspected, your doctor can swab your throat and perform an appropriate quick test.

The following symptoms may occur concurrently with chronic pharyngitis:
- Dryness of the throat
- Constant desire to clear one's throat or swallow
- Feeling of obstruction in the throat
- Dry cough
Upon examination, the mucous membrane is usually dry and reddened.

Pharyngitis: Treatment
Various treatment options are available for pharyngitis.
In the case of acute pharyngitis, the primary concern is targeted and rapid relief from a sore throat and swallowing difficulties. This is particularly true if bacterial pathogens settle on the viral infection. In the case of a sore throat and swallowing difficulties, this makes it all the more important to rely on a medicine that also fights bacterial pathogens.
The unique active ingredient formula in Dorithricin® has been optimised to meet these diverse needs and is therefore perfectly suited for the treatment of acute pharyngitis.
Dorithricin® alleviates pain, fights bacteria and viruses2 and slows down the infection
Dorithricin® contains the natural anti-infective tyrothricin, which not only has antiviral properties but also specifically targets bacterial pathogens. Developing a resistance need not be feared. Tyrothricin additionally has local immune-stimulating properties. In addition, Dorithricin® contains two other active ingredients: A local antiseptic supports the effect of tyrothricin, while a local analgesic provides rapid and long-lasting relief of a sore throat and swallowing difficulties, both of which are typical of pharyngitis.
Excellent: Thanks to the precise dosage ("as much as necessary, as little as possible"), the pain is quickly alleviated without causing unpleasant numbness.
Dorithricin® is extremely well tolerated and suitable for children as soon as they are able to suck on lozenges without the risk of choking.

- Works within minutes1
- Lasts for hours1
- Fights bacteria and viruses2
![]() Important:
Important:
If you suspect you have chronic pharyngitis or if a sore throat persists for more than 3 days, consult your doctor.
Dorithricin®:
Can be used in any phase of pharyngitis
Are you experiencing the first signs of pharyngitis? Then you should start using Dorithricin® right away. This is the best way to improve your chances of slowing down the infection before a sore throat gets worse.
In principle, however, you can also start taking Dorithricin® at a later stage of pharyngitis – that is, even if you already have severe throat pain and/or swallowing difficulties.
Possible phases of pharyngitis and when to take Dorithricin®



